Voici un nouveau tutoriel afin d’installer le module camera V2 de 8 méga pixel sur le robot MRPi1 : installer la camera V2 Pi
Avancement de la production du robot MRPi1
Voici quelques photos de l’avancement de la production du robot MRPi1:
Roues
Visserie
Pi & support
Voici le détails sur la conception & fabrication du robot MRPi1 :
- Conception du robot MRPi1 : Bretagne,
- Développement du robot : Bretagne,
- Fabrication du PCB de la carte de contrôle : Allemagne,
- Fabrication mécanique : Bretagne
- Assemblage des composants CMS de la carte de contrôle : Allemagne,
- Assemblage des composants trad de la carte de contrôle : Bretagne,
- Assemblage du robot : Bretagne,
Un choix a été fait pour réaliser une production la plus local possible.
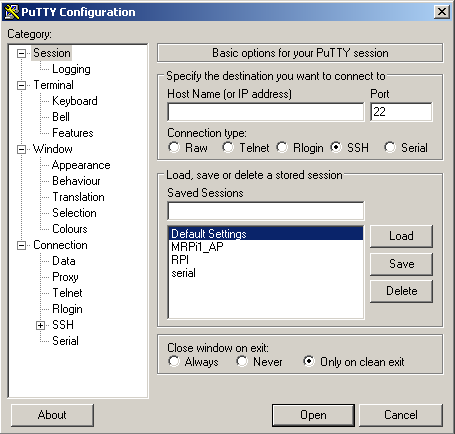
Utiliser Putty en communication série
Voici un petit tutoriel pour utiliser le logiciel Putty en mode série.
Putty est un logiciel client SSH, telnet et peut aussi servir de terminal de liaison série sous Windows. Je l’utilise pour débugger des cartes électroniques avec une liaison USB-série (FT232).
- Démarrer le logiciel Putty :
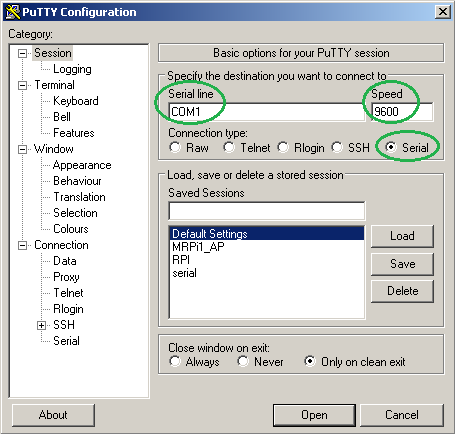
- Sélectionner Serial comme type de connexion :
- Serial Line : le nom du port COM
- Speed : vitesse en baud
Configuration pour la saisie des commandes en entrée :
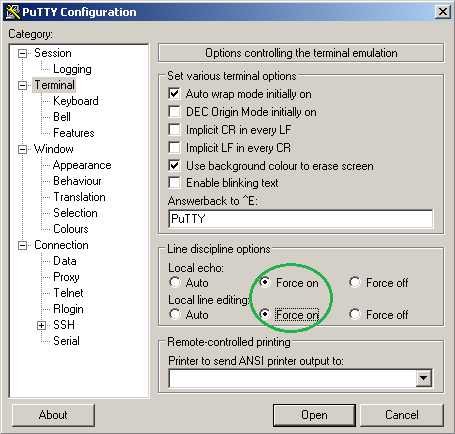
- Sélectionner l’onglet Terminal :
Dans la partie Line discipline options :
- Local echo : Force on
- Local line editing : Force on
- Vous pouvez ensuite ouvrir la connexion :
Fin du tuto !
New video : MRPi1 gripper
Questionnaire sur le robot MRPi1
Un questionnaire en ligne sur le robot MPRi1 :http://shop.macerobotics.com/
Je vous remercie de votre participation.
Streaming vidéo avec la camera Pi
Nouveau tutoriel pour réaliser du streaming vidéo avec la camera Pi sur la carte Raspberry Pi : http://fr.macerobotics.com/developpeur/tutoriels/streaming-video-avec-la-camera-pi/
Rencontres Nationales Raspberry Pi à Nevers
Je vous informe que l’entreprise Mace Robotics sera présent le samedi 30 avril à la première rencontre Nationales Raspberry Pi à Nevers.

Information : http://adn.agglo-nevers.net/index.php/rendez-vous/1-premieres-rencontre-nationales-raspberry-pi
MRPi1 – Course de robot autonome
Nouvelle vidéo, une course de deux robots MRPi1 complétement autonome :
- Un robot MRPi1 version Raspberry Pi,
- Un robot MRPi1 version Arduino,
Les deux robots sont programmés pour suivre le chemin tous en évitant les obstacles. Le robot MRPi1 version Raspberry Pi est programmer en langage Python et la version arduino en langage arduino.
Voici le programme en langage Python pour le MRPi1 Raspberry Pi :
# importez la librairie du robot MRPi1 from mrpi1_lib import * import time # initialisation de la vitesse speedFast=50 speedSlow=30 # seuil détection obstacle limit_obs = 300 try: while 1: # lecture des capteurs de proximité prox1 = proxSensor(1) prox2 = proxSensor(2) prox3 = proxSensor(3) prox4 = proxSensor(4) prox5 = proxSensor(5) prox6 = proxSensor(6) # si obstacle présent sur tous les capteurs if prox1>limit_obs and prox2>limit_obs and prox3>limit_obs and prox4>limit_obs and prox5>limit_obs and prox6>limit_obs: # tourner à droite turnRight(speedSlow) elif prox4>limit_obs or prox5>limit_obs or prox6>limit_obs: # si obstacle à droite, tourner à gauche turnLeft(speedSlow) elif prox1>limit_obs or prox2>limit_obs or prox3>limit_obs: # si obstacle à gauche, tourner à droite turnRight(speedSlow) else: # sinon avancer forward(speedFast) time.sleep(0.4) except: stop() exit()
Le programme en langage arduino pour le MRPi1 version Arduino :
// librairies du robot MRPi1
#include <mrpi1_arduino.h>
// variables pour les capteurs de proximité
int prox1;
int prox2;
int prox3;
int prox4;
int prox5;
int prox6;
// initialisation de la vitesse
int speed = 60;
// initialisation de seuil des obstacles
int limit_obs = 300;
void setup()
{
// initialisation du port série
Serial.begin(115200);
}
void loop()
{
// lecture des capteurs de proximité
prox1 = proxSensor(1);
prox2 = proxSensor(2);
prox3 = proxSensor(3);
prox4 = proxSensor(4);
prox5 = proxSensor(5);
prox6 = proxSensor(6);
// Si obstacles présent sur tous les capteurs
if((prox1 > limit_obs) and (prox2 > limit_obs)and (prox3 > limit_obs) and (prox4 > limit_obs) and (prox5 > limit_obs) and (prox6 > limit_obs))
{
// reculer
back(speed);
}
else
{
// si obstacle à gauche
if((prox1 > limit_obs) and (prox2 > limit_obs))
{
// tourner à droite
turnRight(speed);
}
else
{
// si obstacle à droite
if((prox6 > limit_obs) or (prox5 > limit_obs) or (prox4 > limit_obs))
{
// tourner à gauche
turnLeft(speed);
}
else
{
// si obstacle à gauche
if((prox1 > limit_obs) or (prox2 > limit_obs) or (prox3 > limit_obs))
{
// tourner à droite
turnRight(speed);
}
else
{
// sinon avancer
forward(speed);
}
}
}
}
}
Nouveau tutoriel pour la version MRPi1 Arduino
- Gestion des leds du robot MPRi1 version arduino.
- Utilisation de l’IDE Arduino
http://fr.macerobotics.com/developpeur/tutoriels/gestion-des-leds-version-arduino/
MRPi1 – delivery robot
New video of MRPi1 robot :
- Python program,
- Autonomous robot,
- Control the position with remote control,
The python program :
from mrpi1_lib import *
import time
ir = 0;
state = 0
controlEnable()
while 1:
# read the infrared receiver
ir = irReceiver()
time.sleep(0.2)
if(ir == 1) and (state == 0):
forwardC(10,400)
state = 1
if(ir == 2) and (state == 0):
forwardC(10,800)
state = 2
if(ir == 3) and (state == 0):
forwardC(10,1600)
state = 3
if(ir == 3) and (state == 1):
forwardC(10,1200)
state = 3
if(ir == 3) and (state == 2):
forwardC(10,800)
state = 3
if(ir == 2) and (state == 1):
forwardC(10,400)
state = 2
if(ir == 1) and (state == 2):
backC(10,400)
state = 1
if(ir == 1) and (state == 3):
backC(10,1200)
state = 1
if(ir == 2) and (state == 3):
backC(10,800)
state = 2
if(ir == 0) and (state == 3):
backC(10,1600)
state = 0
if(ir == 0) and (state == 2):
backC(10,800)
state = 0
if(ir == 0) and (state == 1):
backC(10,400)
state = 0