Des roues de 34 mm de diamètre sont disponibles en boutique :
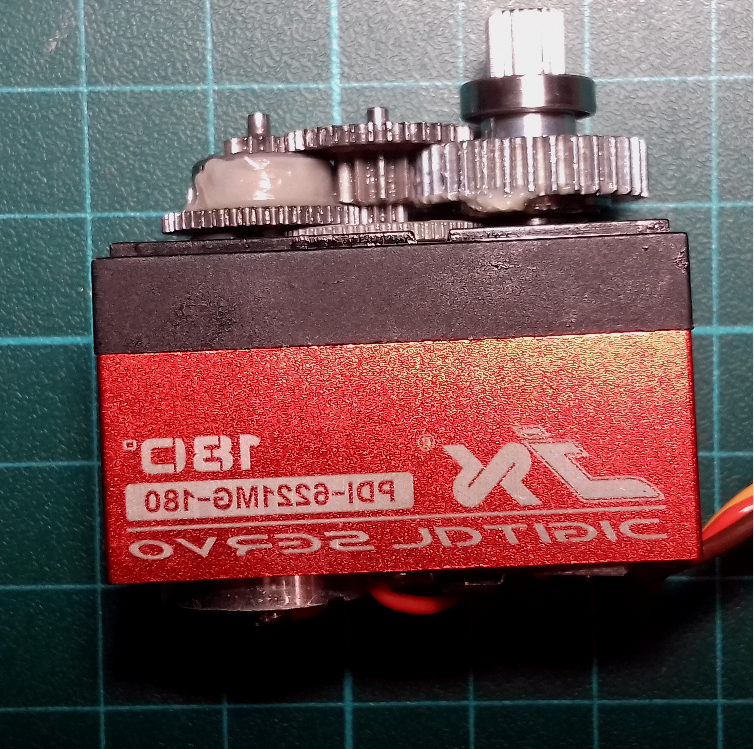
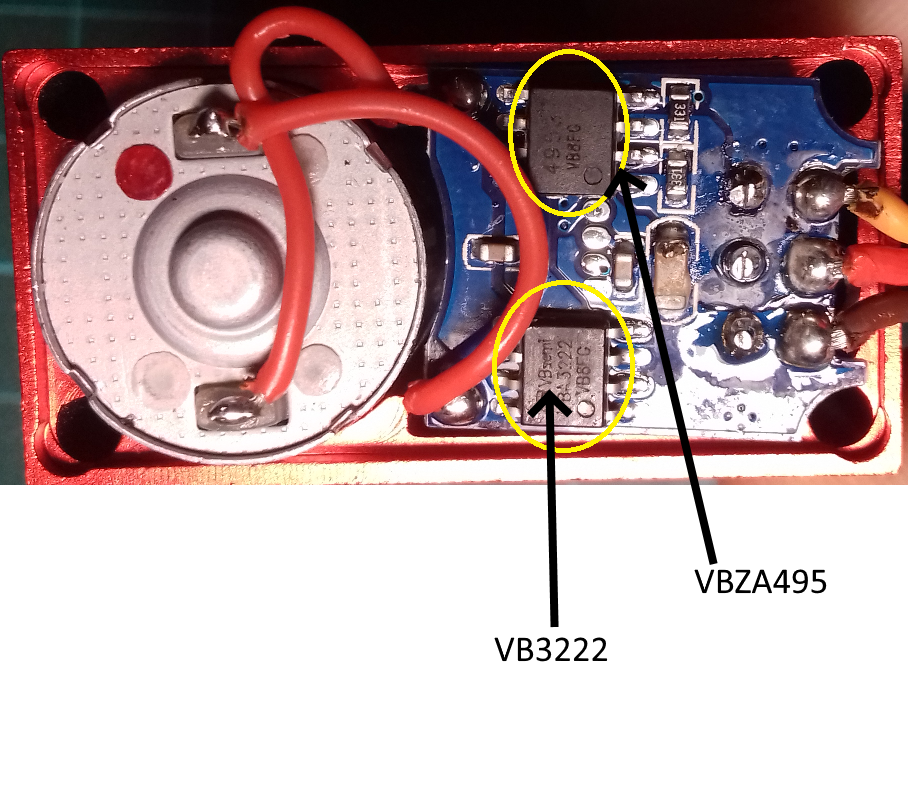
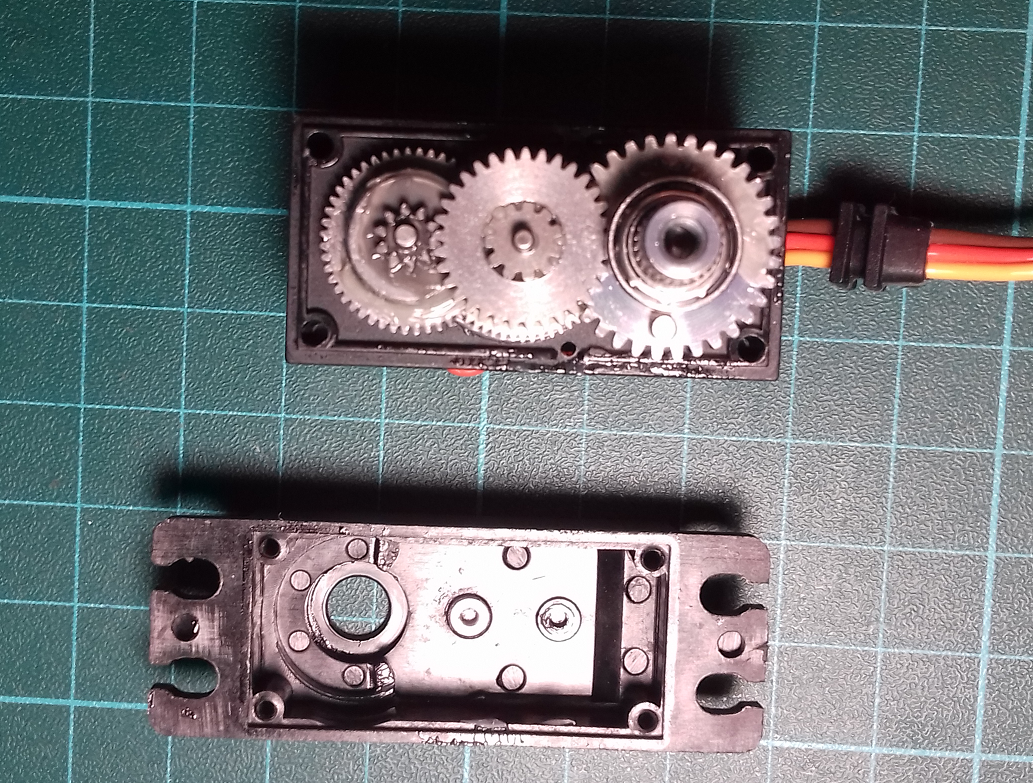
Inside PDI-6221MG servomotor
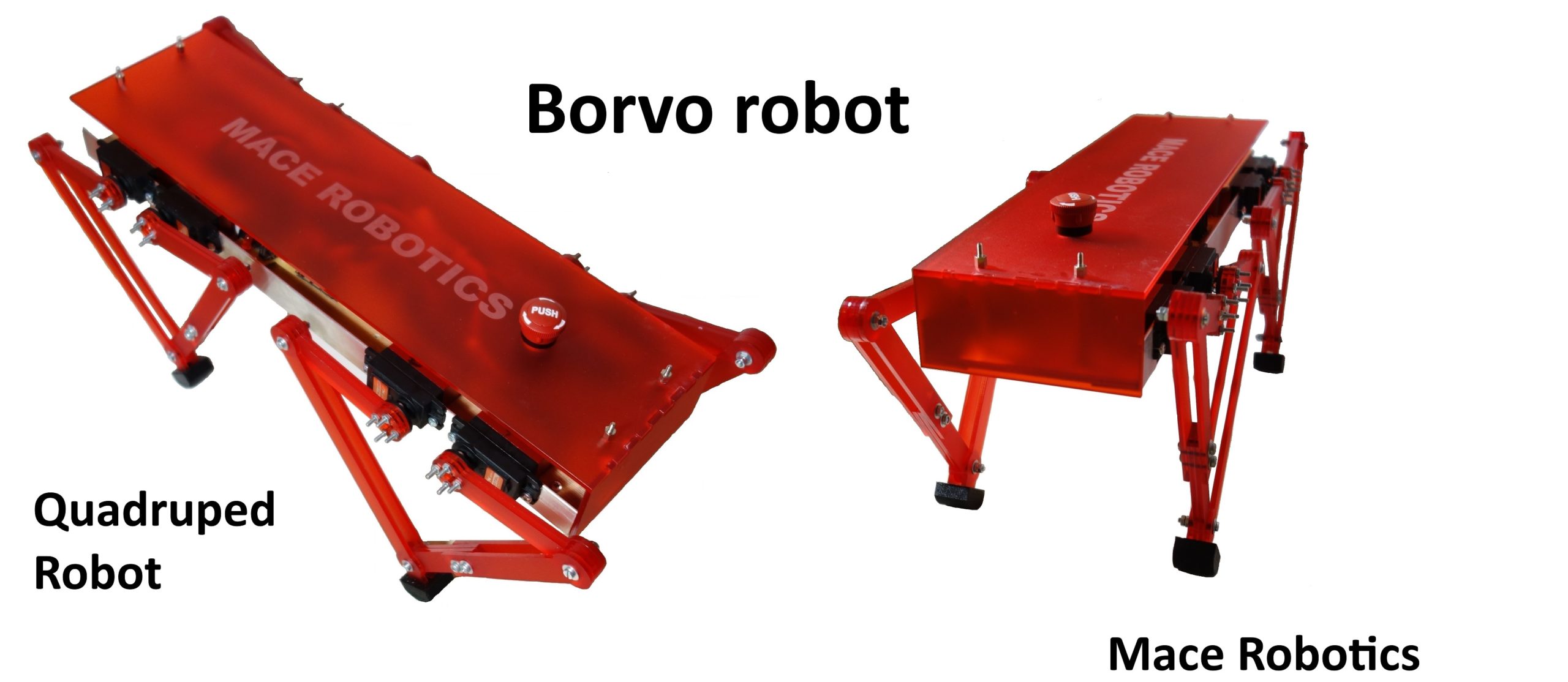
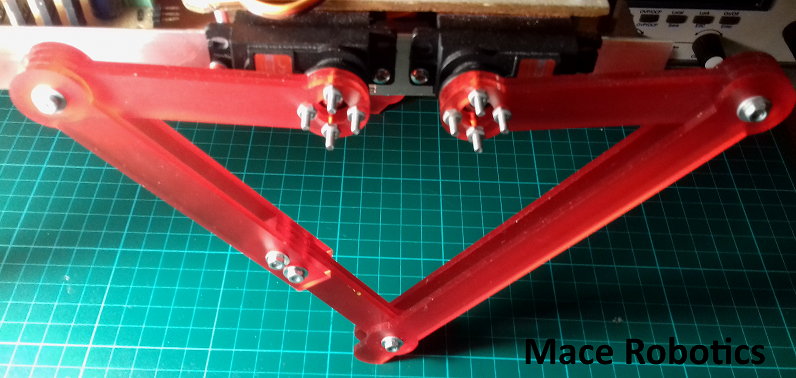
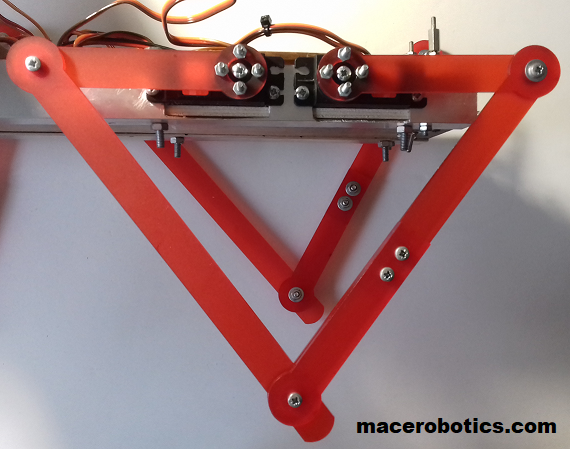
Nouvelle structure
Une nouvelle structure mécanique pour le robot quadrupède BORVO:
- structure en pmma 3 mm
- pied souple en impression 3D
- pattes plus rigide
Plus d’informations sur le projet : https://fr.macerobotics.com/robot-borvo/
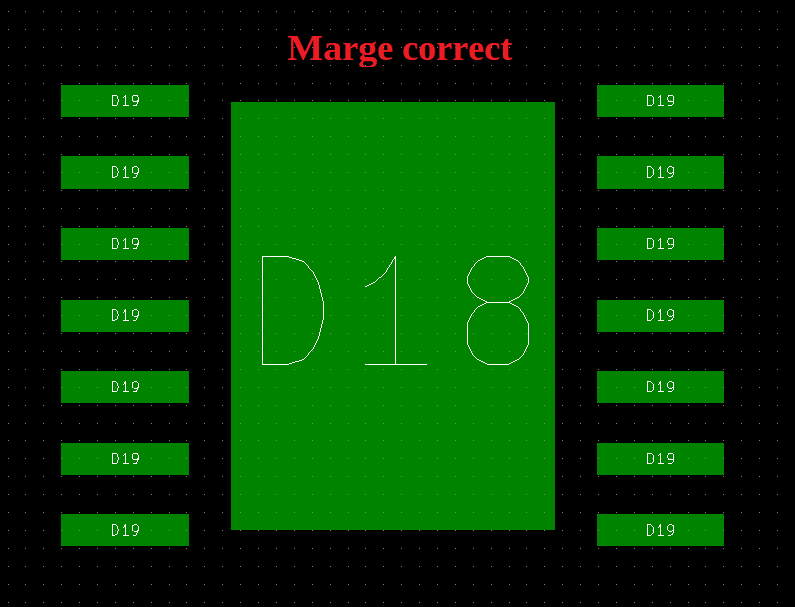
Modifier la marge du Vernis épargne sous KiCad
Le vernis épargne ?
Le vernis épargne est une fine couche de résine polymère souvent de couleur verte permettant de protéger le cuivre de l’oxydation et empêcher la formation de court-circuit entre les pistes ou pads d’un composant CMS.
Problème possible
Une marge du vernis épargne trop grande peut supprimer l’épargne nécessaire entre les pads d’un composant CMS :
Couche masque de soudure coté top (F-Mask), fichier gerber .gts :
Les pads du composants seront bien entourés de vernis épargne :
Les pads du composants ne seront pas bien entourés de vernis épargne :
Modifier la marge
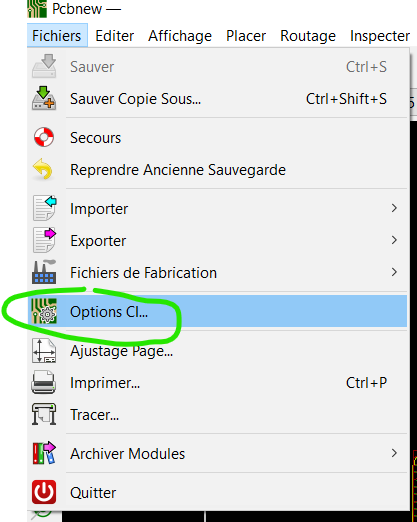
Dans PCBnew :
- Fichiers -> Options CI
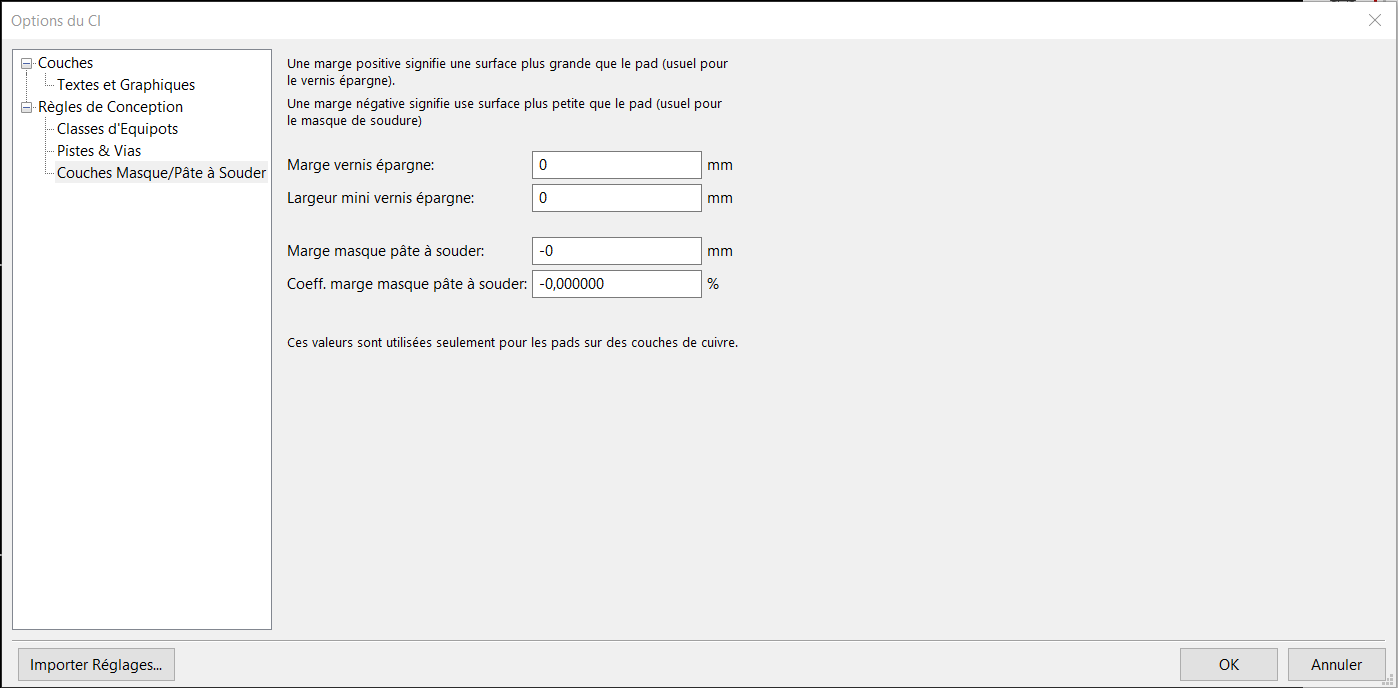
Options du CI :
Fin.
Borvo robot quadrupède – mise à jour
The new legs for the Borvo robot – version 2
The new legs for the Borvo robot
New foot
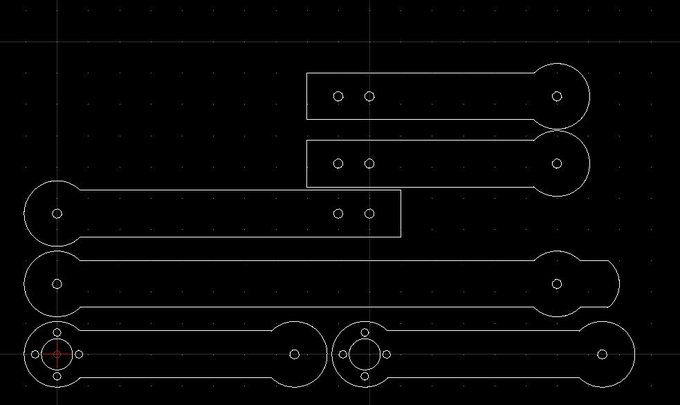
I draw foot for the quadruped robot with FreeCAD software : 
New leg design for the quadruped robot:
New leg design for the Borvo quadruped robot :
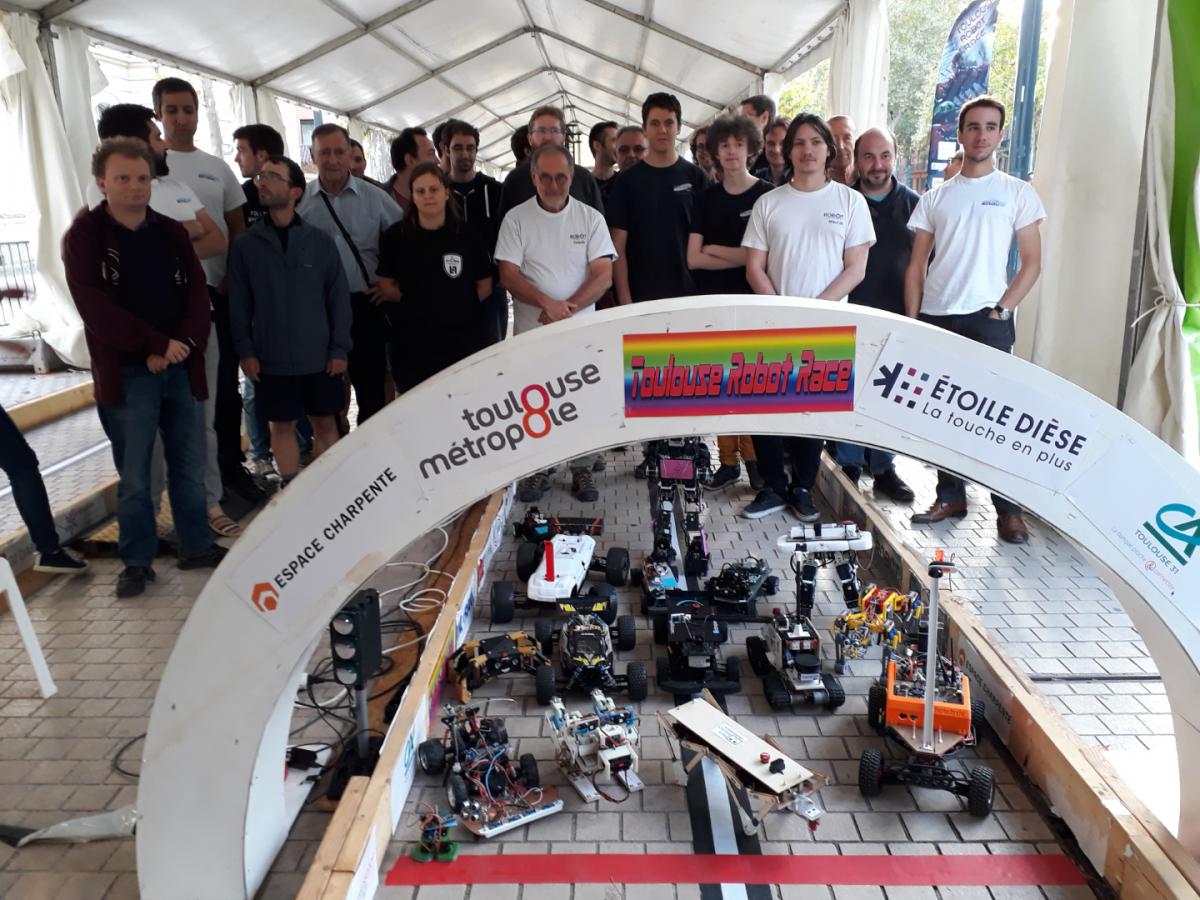
Toulouse Robot Race 2019
Mace Robotics a participé à la Toulouse Robot Race 2019 dans la catégorie multipattes avec le robot quadrupède Borvo. Le robot Borvo à terminer à la 2éme place dans la catégorie multipattes.
Robot Borvo
Caractéristiques du robot quadrupède Borvo :
- 8 servomoteurs JX PDI-6221MG 20KG
- Microcontrôleur : teensys 3.5 (compatible avec Arduino)
- 2x capteurs de distance VL53L0X à droite et gauche du robot. Pour le recalage en orientation du robot avec les bordures de la piste.
- 1 capteur LIDAR TFmini-Plus pour la détection du portique de la fin de la course.
- Batterie LiPo 2S
- Mécanique : bois peuplier 3 mm (découpé au laser)
- Bouton ON/OFF
- Switch start
- Bouton arrêt urgence
- Taille : 400 x 105 x 160 mm
Voici quelques robots rencontré à la Toulouse Robot Race :
- Robot humanoïde de l’équipe Rhoban (http://rhoban.com/fr/)
- Voiture autonome avec carte NVDIA Jetson GPU (équipe TurboDroid )
- Bipède avec servomoteurs dynamixel (plus d’info):
La piste de course :
Les participants à la Toulouse Robot Race 2019 :

Plus d’informations :