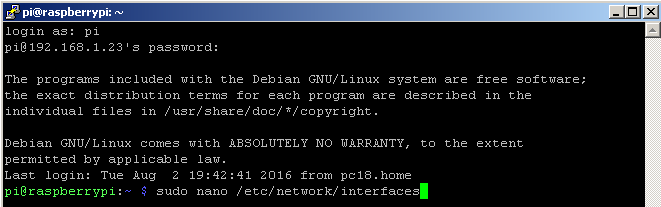
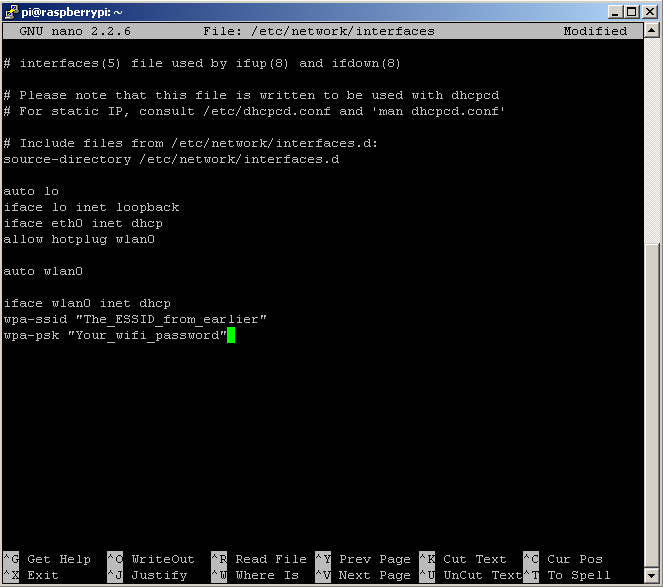
Dans ce tutoriel vous allez créer votre propre modélisation de robot mobile avec l’aide d’un fichier URDF. Ce tutoriel nécessite l’installation de ROS sur Ubuntu.
Système :
Crée votre workspace
Une fois sur Ubuntu, vous pouvez ouvrir un terminal.
La première chose à faire et de créer votre workspace pour la création de votre robot.
- Commande pour crée le dosser MyRobot_ws :
$ mkdir -p ~/MyRobot_ws/src
$ cd ~/MyRobot_ws/src
- Commande pour initialiser le workspace :
$ catkin_init_workspace
Crée votre package
- Commande pour crée le package MyRobot :
$ cd ~/MyRobot_ws/src
$ catkin_create_pkg MyRobot
Maintenant que votre environnement est près vous pouvez crée la modélisation du robot.
Modélisation du robot
Cette partie va vous permettre de réaliser la modélisation du petit robot mobile de type différentielle :
- 2 roues
- 1 ball-caster
- 1 chassis
Modélisation du châssis
- Crée un fichier de type URDF (Unified Robot Description Format) :
$ gedit ~/MyRobot_ws/src/MyRobot/MyRobot.urdf
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot name="MyRobot">
<link name="base_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="0.035" radius="0.05"/>
</geometry>
<material name="white">
<color rgba="1 1 1 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
</link>
</robot>
- Enregistrer le fichier
- Commande pour visualisez le châssis en 3D avec l’outils Rviz :
$ roslaunch urdf_tutorial display.launch model:=MyRobot.urdf
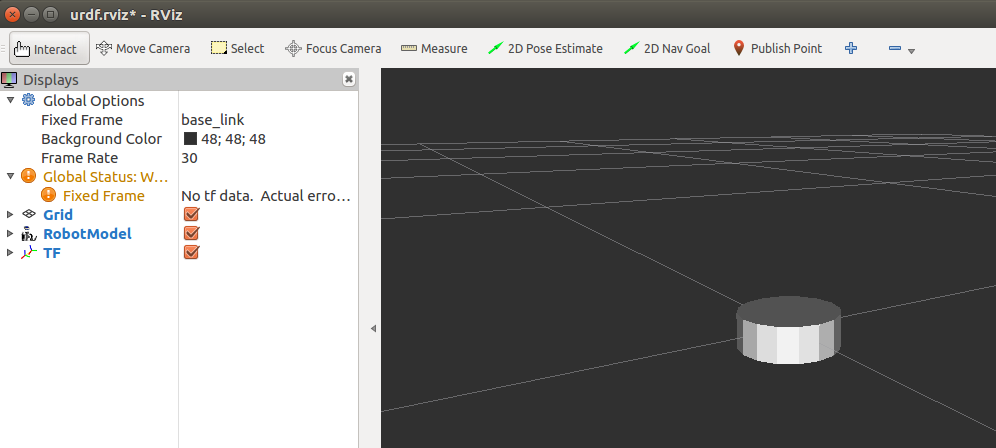
Modélisation des roues du robot mobile
- Modélisation de la roue droite :
<link name="right_wheel">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="0.005" radius="0.016"/>
</geometry>
<material name="black">
<color rgba="0 0 0 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
</link>
- Modélisation du lien entre la roue droite et le châssis :
<joint name="right_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<axis xyz="0 0 1"/>
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="right_wheel"/>
<origin rpy="0 -1.5708 0" xyz="0.05 0 -0.0105"/>
</joint>
- Modélisation de la roue gauche :
<link name="left_wheel">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="0.005" radius="0.016"/>
</geometry>
<material name="black">
<color rgba="0 0 0 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
</link>
- Modélisation du lien entre la roue gauche et le châssis :
<joint name="left_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<axis xyz="0 0 1"/>
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="left_wheel"/>
<origin rpy="0 -1.5708 0" xyz="-0.05 0 -0.0105"/>
</joint>
- Visualisation du résultat avec Rviz :
$ roslaunch urdf_tutorial display.launch model:=MyRobot.urdf
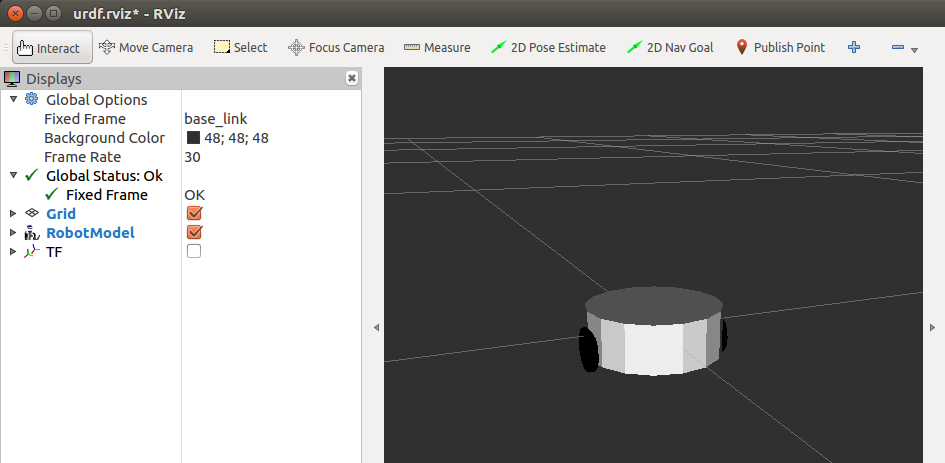
Avec Rviz vous pouvez visualiser le robot avec les deux roues.
Modélisation de la ball caster
- Modélisation de la ball-caster :
<link name="caster_wheel">
<visual>
<geometry>
<sphere radius="0.0045"/>
</geometry>
<material name="black"/>
</visual>
</link>
- Modélisation du lien entre la roue gauche et le châssis :
<joint name="caster_wheel_joint" type="fixed">
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="caster_wheel"/>
<origin rpy="0 0 0" xyz="0 0.025 -0.022"/>
</joint>
- Visualisation du résultat avec Rviz :
$ roslaunch urdf_tutorial display.launch model:=MyRobot.urdf
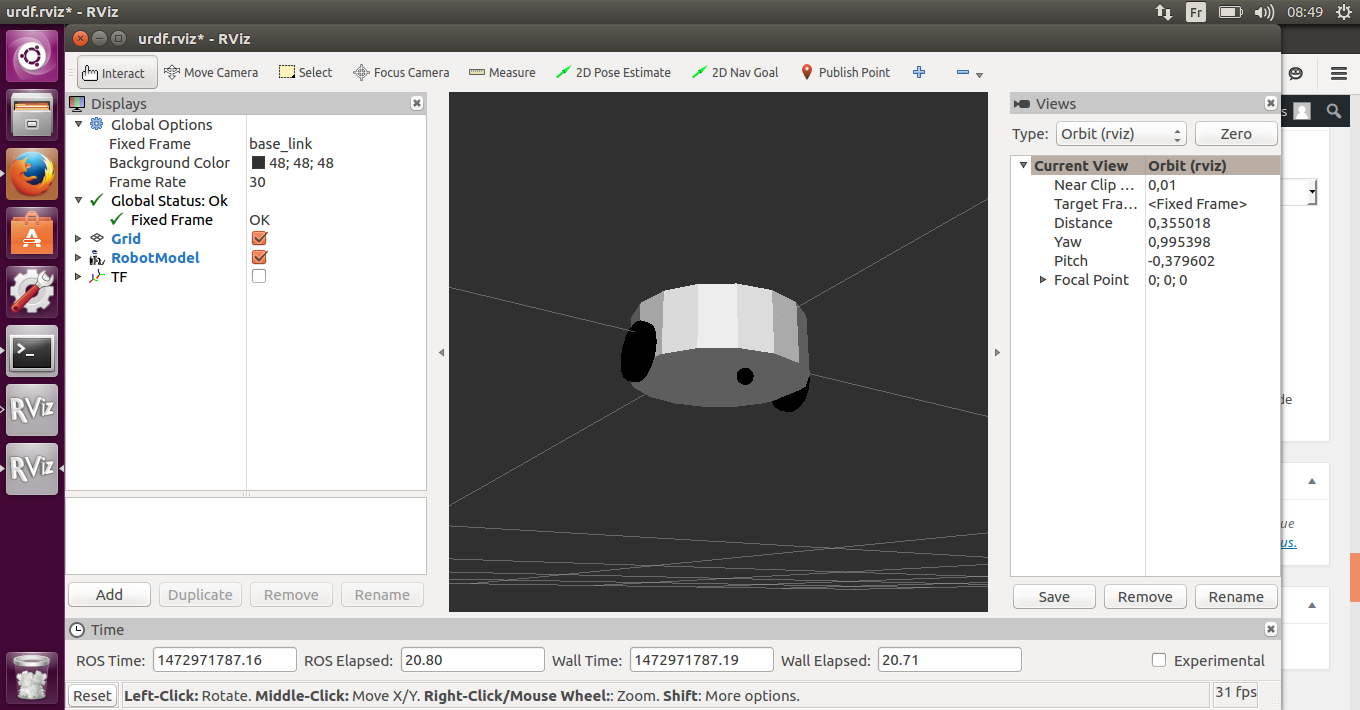
Fin de la partie n°1.