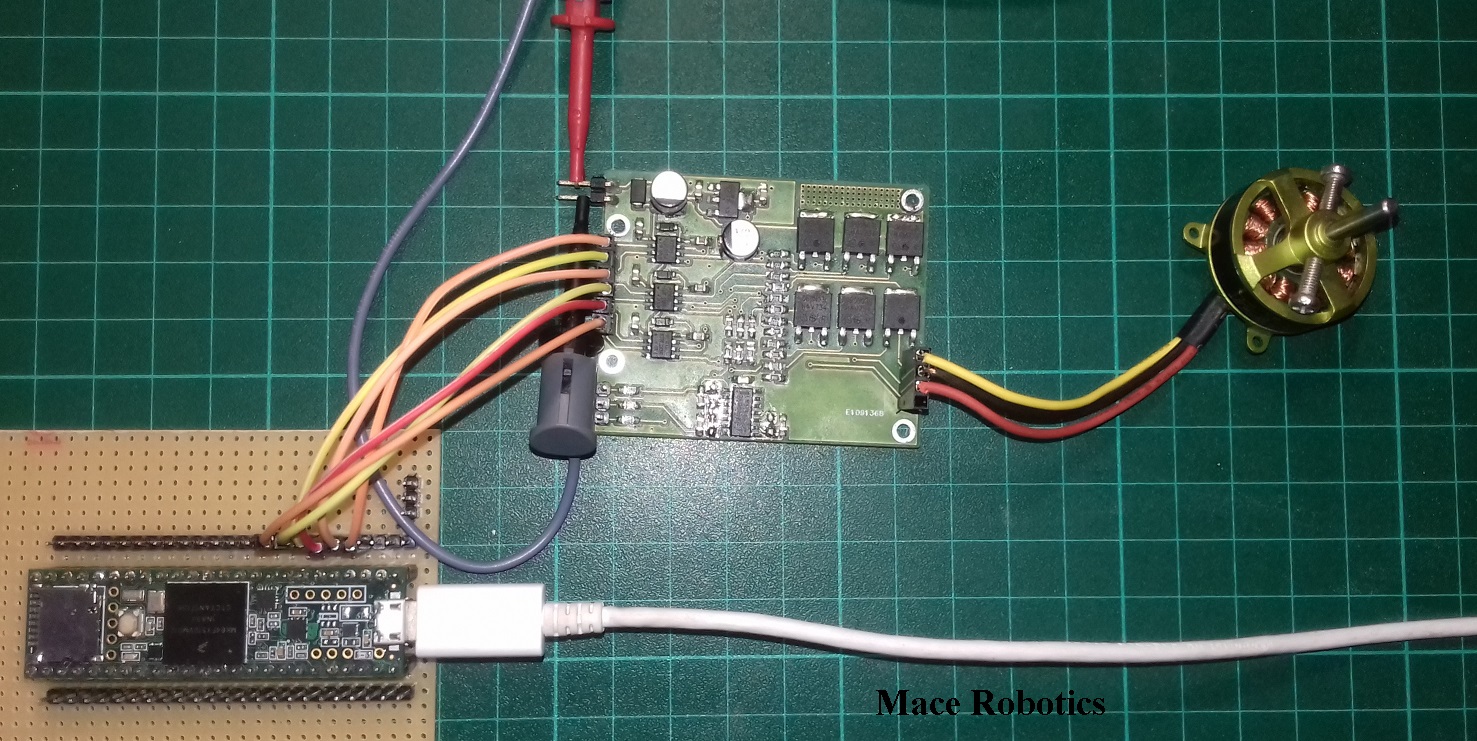
Contrôle moteur BLDC
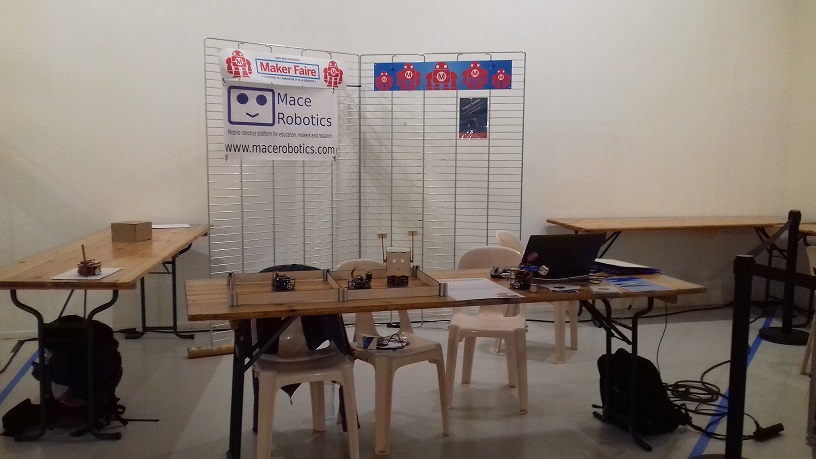
Maker Faire Lille 2019
KiCad : création des fichiers de fabrication d’un PCB
Kicad version : 5.0.1
Un tutoriel pour générer les fichiers de fabrication d’un circuit imprimé sous le logiciel libre KiCad.
- Les fichiers gerbers (RS-274X) : format de fichier standard pour la fabrication des circuits imprimés.
- Fichier des perçages
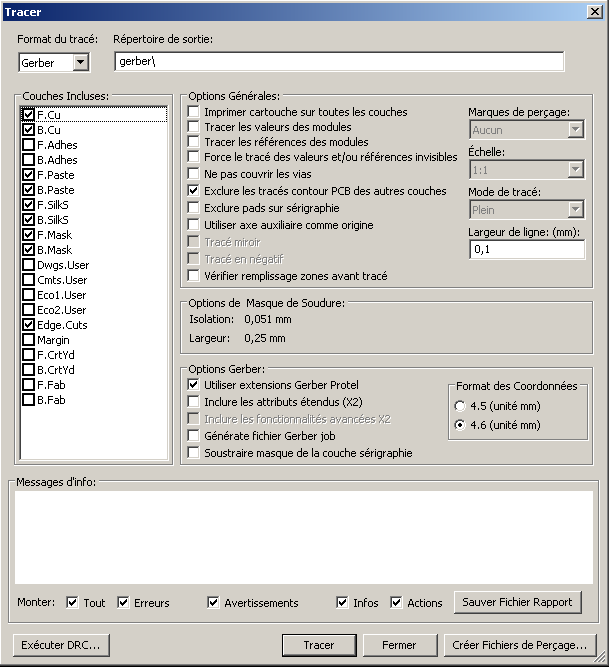
Dans Pcbnew :
Après avoir terminer le routage de votre carte électronique :
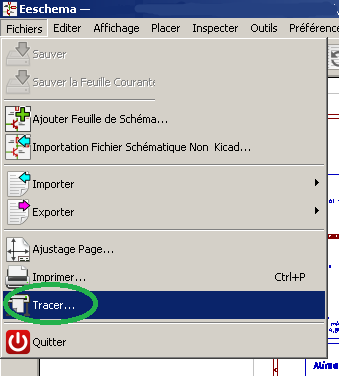
- Fichiers->Tracer
Exemple pour un circuit imprimé avec 2 couches :
- F.Cu : couche cuivre dessus (TOP)
- B.Cu : couche cuivre dessous (BOTTOM)
- F.Paste : couche pâte à souder du dessus (TOP)
- B.Paste : couche pâte à souder du dessous (BOTTOM)
- F.SilkS : sérigraphie sur le dessus (TOP)
- B.SilkS : sérigraphie sur le dessous (TOP)
- F.Mask : couche vernis épargne ou masque de soudure (TOP)
- B.Mask : couche vernis épargne (BOTTOM)
- Edge.Cuts : couche du contours du circuit imprimé
- Puis, cliquez sur «Tracer».
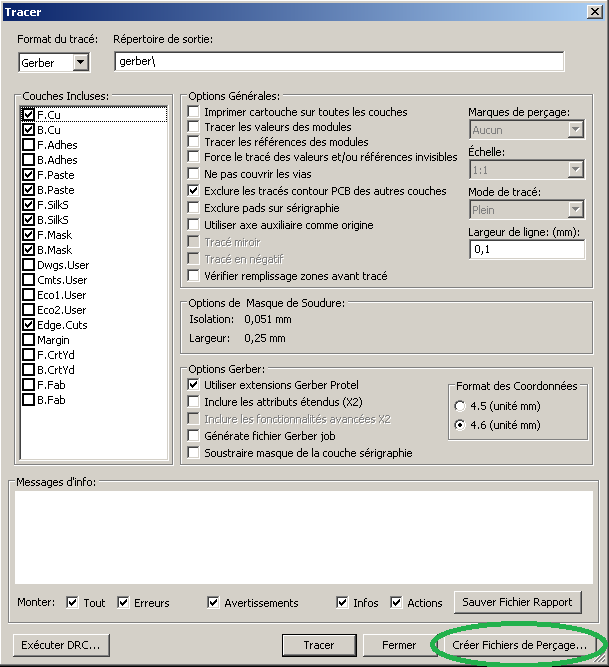
- Ensuite, crée le fichier de perçage:
- Configuration pour le fichier de perçage:
- Format excellon : formats standard pour la commande numérique des perceuses pour la fabrication des circuits imprimés.
Fin du tuto !
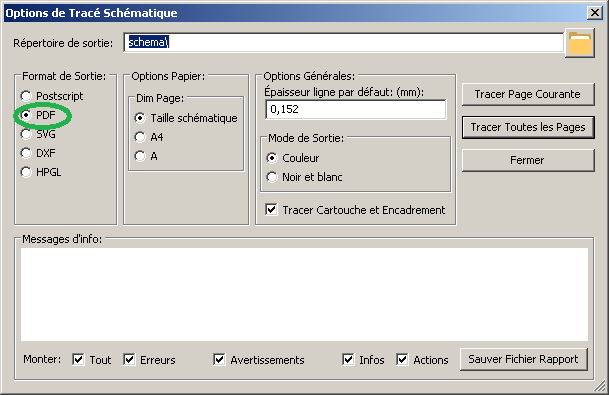
Kicad : création d’un PDF
MRPiZ – suivie de ligne avec openCV & python
Ce tutorial présente l’implémentation d’un suivi de ligne pour le robot mobile MRPiZ.
Matériel nécessaire
- Un robot MRPiZ
- Une caméra compatible, idéalement grand angle.
Logiciels nécessaire
- Python 2.7 (déja installé par défaut),
- La bibliothèque Python MRPiZ (déja installée par défaut),
- OpenCV pour python
Activation de video4linux
Deux méthodes sont possibles pour accéder à la caméra:
- PiCamera: la méthode la plus répandue, mais lente car il est nécessaire de transformer l’image pour la mettre au bon format,
- v4l: qui s’interface directement avec OpenCV, c’est la méthode choisie pour ce tutorial.
Il nous faut donc activer v4l:
$ sudo modprobe bcm2835-v4l2
Le suivi de ligne
Le fichier complet se trouve dans Software/Python/tutorials/line_follower/line.py.
Warning
Utilisez CTRL+C pour arrêter le robot.
Importation des modules
import numpy as np
import cv2
import sys
from mrpiZ_lib import *
Paramétrés globaux
# image size
WIDTH = 640
HEIGHT = 480
# turn coeff
COEFF = 0.05
# base robot speed in straight line
SPEED = 30
Activation de la caméra
Pour améliorer les performances, la résolution est réduite à 640 pixels en largeur et 480 en hauteur.
video_capture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
video_capture.set(3, WIDTH)
video_capture.set(4, HEIGHT)
Boucle principale
La boucle principale va fonctionner à l’infini, pour l’arrêter il faudra appuyer sur CTRL+C.
try:
while(True):
Capture de l’image
Première étape, on commence par capturer une image.
# Capture the frames
ret, frame = video_capture.read()
Voici un exemple d’image capturée:
Suppression de la partie haute
Pour améliorer les performances, on ne va garder que la partie basse de l’image:
# Crop the image
# Keep the 100 lower pixels
crop_img = frame[379:480, 0:640]
Niveaux de gris
Ensuite on passe l’image en niveaux de gris:
# Convert to grayscale
gray = cv2.cvtColor(crop_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
Flou
Un filtre afin de rendre flou les lignes de l’image est appliqué, il permet de rendre plus efficace les étapes suivantes:
# Gaussian blur
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray,(5,5),0)
Seuillage
Ensuite on va filtrer les parties claires de l’image pour ne garder les parties noires, pour cela, un filtre de seuillage est appliqué:
# Color thresholding
ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(blur,60,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
Détection de contours
Ensuite, on va utiliser openCV pour détecter les contours:
# Find the contours of the frame
contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh.copy(), 1, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
Extraction du plus gros contour
Il nous faut ensuite extraire la ligne la plus large trouvée afin d’éliminer les fausses détections:
# Find the biggest contour (if detected)
if len(contours) > 0:
c = max(contours, key=cv2.contourArea)
M = cv2.moments(c)
# Skip to avoid div by zero
if int(M['m00']) == 0:
continue
Calcul du milieu de la ligne
Une fois les contours de la ligne détectée, on calcul le centre de la ligne, c’est la que l’on veut que le robot aille:
# Get the line center
cx = int(M['m10']/M['m00'])
cy = int(M['m01']/M['m00'])
Contrôle des moteurs
Une correction proportionnelle à la différence entre la position de la ligne et le milieu de l’image est calculée. Les moteurs sont ensuite commandés pour ralentir un des moteurs et accélérer l’autre, ceci afin de faire tourner le robot en direction du centre de la ligne.
delta = COEFF * (cx - 320)
motorRight(0, SPEED - delta)
motorLeft(0, SPEED + delta)
Clavier
Enfin, deux lignes de code permettent d’arrêter le robot quand on appuie sur CTRL+C.
except KeyboardInterrupt:
stop()
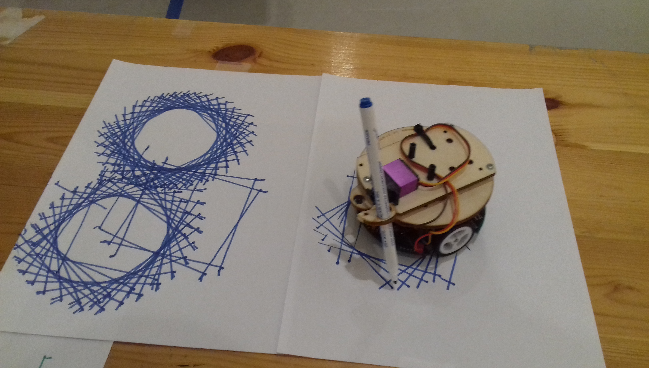
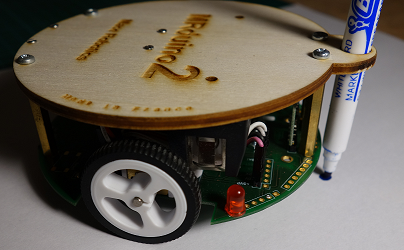
Dessin avec MRduino2 & Blockly
Tutoriel pour faire dessiner le robot MRduino2.
Matériel nécessaire:
- Un feutre de couleur
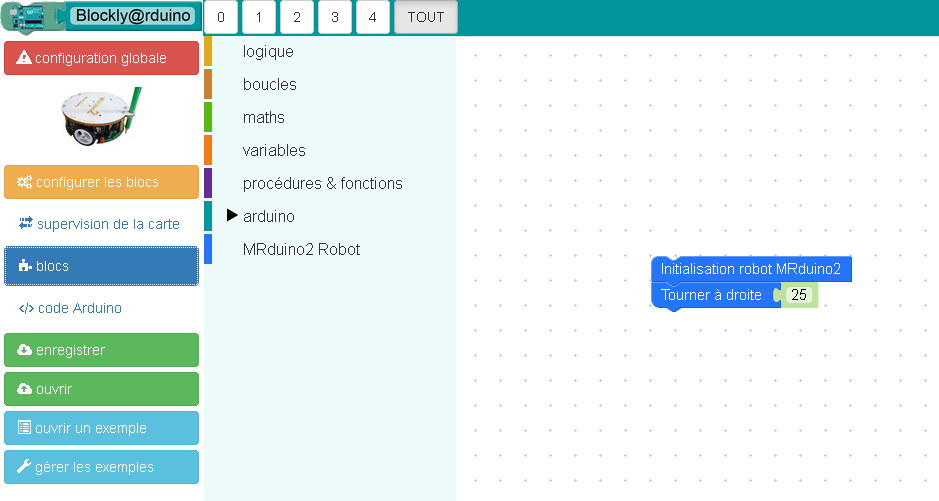
Dessiner un petit cercle
Un simple programme pour faire un cercle :
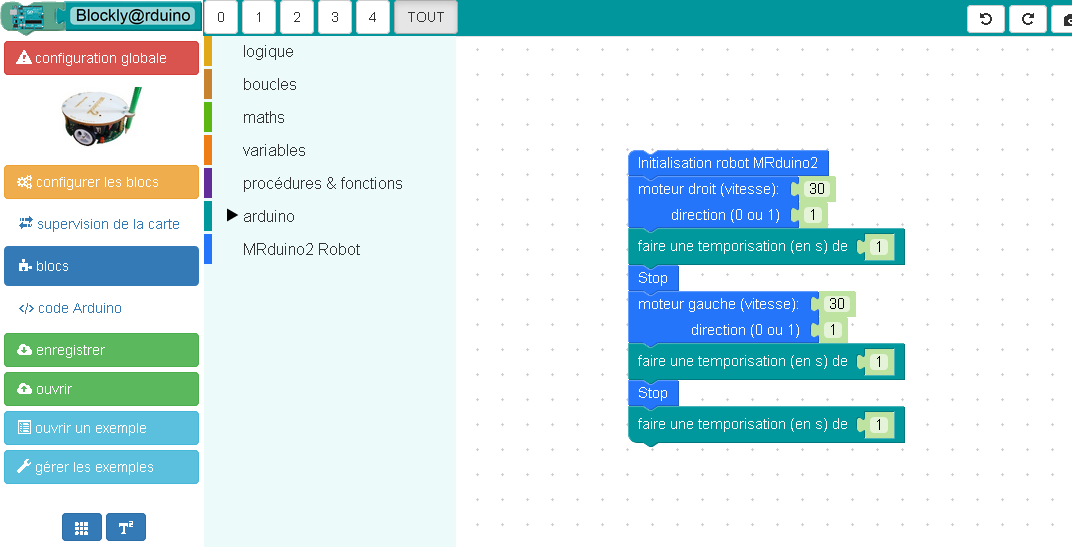
- Le robot tourne sur lui-même vers la droite à une vitesse de 25%.
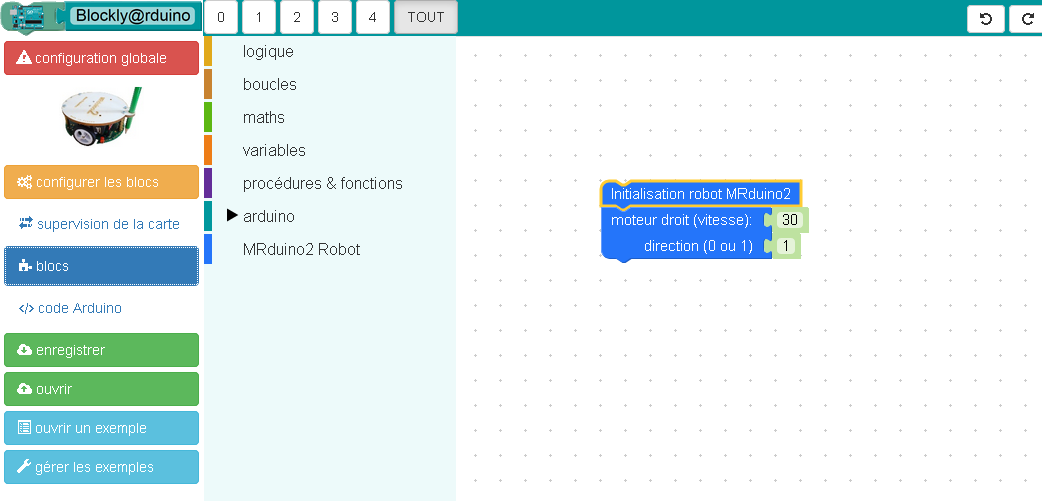
Dessiner un grand cercle
Une autre manière de faire un cercle plus grand en utilisant un seul moteur :
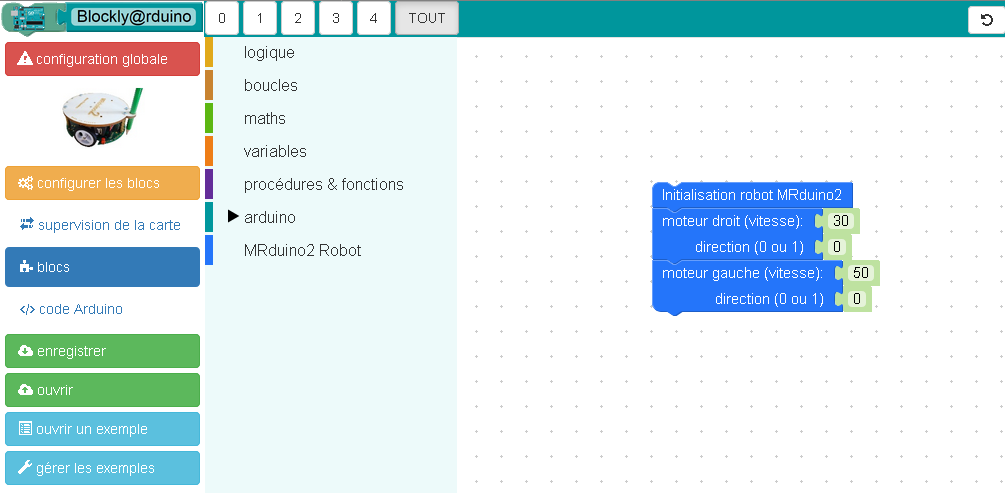
Petit exercice,comment dessiner un très grand cercle ?
La réponse :
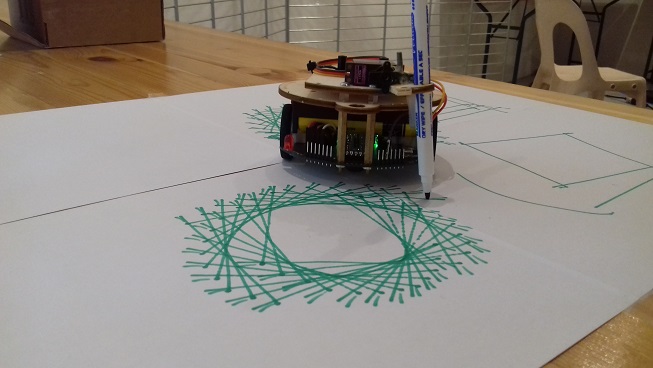
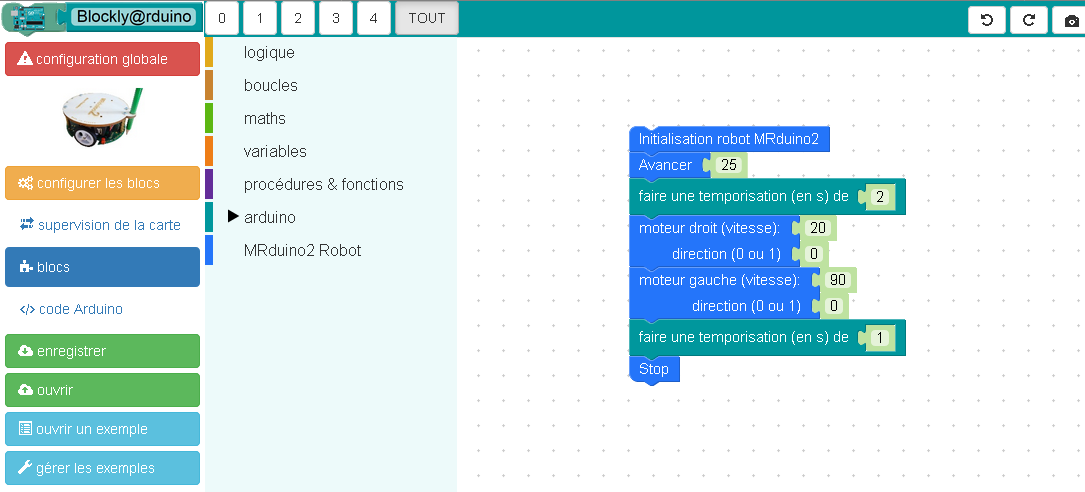
Dessiner des vagues
Un petit programme Blockly pour dessiner des vagues avec le robot MRduino2:
Dessiner un carré (un peu près !)
Un programme pour dessiner un carré :
Fin du tuto, à vous de réaliser vos propres dessins.
Mise à jour – MRduino2
Mise à jour du guide de démarrage du robot MRduino2 le 14/11/2018.
MRduino2 obstacle avoidance
Tutoriel blockly pour le robot MRduino2
Une vidéo pour réaliser un programme de gestion des obstacles avec le langage graphique Blockly :